An investigation of cracking causes in an outlet RTJ flange in ISOMAX unit
A.N. Delavar - RIPI Tehran
(in lingua inglese)
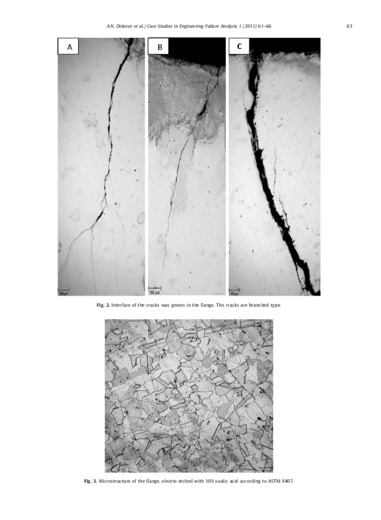
In this case, another source of chloride is anti-seize grease that it is used for fastening of flanges. So a sample of that grease was evaluated according to ASTM D808 method to determine the amount of its chloride. The result showed that there was 0.1 wt.% chloride in the used grease. The entrapped chloride at the groove of RTJ flange because of its geometry get concentrated by evaporation at high operating temperature, and the subsequent cracking of the RTJ groove occurs at areas with applied or residual stress. Above evidences indicated that the flange failed by Cl SCC due to using unqualified anti-seize grease in maintenance procedure.
Fonte: Articolo Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013
Settori: Meccanica
Parole chiave: Flangia
- Maurizio Baltera
- Gianluca Losi
- Gianluca Losi
- Mauro Stien
 English
English